 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 |
Astronomy Picture of the Day |
 APOD: 2023 November 8 – Perseus Galaxy Cluster from Euclid
APOD: 2023 November 8 – Perseus Galaxy Cluster from Euclid
Explanation:
There's a new space telescope in the sky:
Euclid.
Equipped with two large panoramic cameras,
Euclid captures light from the
visible to the near-infrared.
It took five hours of observing for
Euclid's 1.2-meter diameter primary mirror
to capture, through its
sharp optics,
the 1000+ galaxies in the
Perseus cluster, which lies 250 million
light years away.
More than 100,000 galaxies are visible in the background,
some as
far away as 10 billion light years.
The revolutionary nature of
Euclid
lies in the combination of its wide
field of view (twice the area of the full moon),
its high angular resolution
(thanks to its 620 Megapixel camera), and its infrared vision,
which captures both images and
spectra.
Euclid's initial surveys, covering a third of the sky and recording over
2 billion galaxies, will enable a
study of how
dark matter
and
dark energy have shaped
our universe.
 APOD: 2023 May 7 – The Helix Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2023 May 7 – The Helix Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
Will our Sun look like this one day?
The Helix Nebula is one of brightest and closest examples of a
planetary nebula, a gas
cloud created at the end of the life of a Sun-like star.
The outer gasses of the star
expelled into space appear from our
vantage point as if we are looking down a helix.
The remnant central stellar core, destined to become a white dwarf star, glows in light so
energetic
it causes the previously expelled gas to fluoresce.
The Helix Nebula, given a technical designation of
NGC 7293,
lies about 700 light-years away towards the
constellation of the Water Bearer (Aquarius)
and spans about 2.5 light-years.
The featured picture was taken with the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) located atop a
dormant volcano in Hawaii,
USA.
A close-up of the
inner edge of the Helix Nebula shows complex gas knots of
unknown origin.
 APOD: 2022 February 7 - NGC 4651: The Umbrella Galaxy
APOD: 2022 February 7 - NGC 4651: The Umbrella Galaxy
Explanation:
It's raining stars.
What appears to be a giant cosmic umbrella
is now known to be a tidal stream of stars
stripped from a small
satellite galaxy.
The main galaxy, spiral galaxy
NGC 4651,
is about the size of our
Milky Way, while its stellar parasol appears to extend
some 100 thousand light-years above this galaxy's bright disk.
A small galaxy was likely torn apart by
repeated encounters as
it swept back and forth on eccentric orbits through NGC 4651.
The remaining stars will surely fall back and become part of a
combined larger galaxy
over the next few million years.
The featured image was
captured by the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope
(CFHT) in Hawaii,
USA.
The Umbrella Galaxy lies about 50 million
light-years
distant toward the
well-groomed northern constellation
Coma
Berenices.
 APOD: 2021 May 17 - NGC 4565: Galaxy on Edge
APOD: 2021 May 17 - NGC 4565: Galaxy on Edge
Explanation:
Is our Milky Way Galaxy this thin?
Magnificent spiral galaxy
NGC 4565
is viewed edge-on from planet Earth.
Also known as the Needle Galaxy for its narrow profile, bright
NGC 4565 is a stop on many telescopic tours of the northern sky,
in the faint but well-groomed
constellation Coma
Berenices.
This sharp, colorful image reveals the spiral galaxy's
boxy, bulging
central core cut by
obscuring dust lanes that lace
NGC 4565's thin galactic plane.
An assortment of other
background galaxies is included
in the pretty field of view.
Thought similar in shape to our own
Milky Way Galaxy,
NGC 4565 lies about 40 million
light-years distant and spans
some 100,000 light-years.
Easily spotted with small telescopes,
sky enthusiasts consider
NGC 4565 to be a prominent celestial
masterpiece Messier missed.
 APOD: 2021 May 10 - Star Clusters M35 and NGC 2158
APOD: 2021 May 10 - Star Clusters M35 and NGC 2158
Explanation:
Clusters of stars can be near or far, young or old, diffuse or compact.
The
featured image
shows two quite contrasting
open star clusters
in the same field.
M35,
on the lower left, is relatively nearby at 2800
light years distant, relatively young at 150 million years old, and relatively diffuse, with about 2500 stars spread out over a
volume 30 light years across.
Bright blue stars frequently
distinguish younger open clusters like M35.
Contrastingly,
NGC 2158,
on the upper right, is four times more distant than
M35,
over 10 times older, and much more compact.
NGC 2158's bright blue stars have
self-destructed,
leaving cluster light to be dominated by
older and yellower stars.
In general, open star clusters are found in the plane of
our Milky Way Galaxy, and contain anywhere from 100 to 10,000 stars --
all of which formed at nearly the same time.
Both open clusters M35 and NGC 2158 can be
found together with a small telescope
toward the constellation of the Twins
(Gemini).
 APOD: 2020 November 24 - The Helix Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2020 November 24 - The Helix Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
Will our Sun look like this one day?
The Helix Nebula is one of brightest and closest examples of a
planetary nebula, a gas
cloud created at the end of the life of a Sun-like star.
The outer gasses of the star
expelled into space appear from our
vantage point as if we are looking down a helix.
The remnant central stellar core, destined to become a white dwarf star, glows in light so
energetic
it causes the previously expelled gas to fluoresce.
The Helix Nebula, given a technical designation of
NGC 7293,
lies about 700 light-years away towards the
constellation of the Water Bearer (Aquarius)
and spans about 2.5 light-years.
The featured picture was taken with the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) located atop a dormant volcano in Hawaii,
USA.
A close-up of the
inner edge of the Helix Nebula shows complex gas knots of
unknown origin.
 APOD: 2018 February 6 - Galaxy NGC 474: Shells and Star Streams
APOD: 2018 February 6 - Galaxy NGC 474: Shells and Star Streams
Explanation:
What's happening to galaxy NGC 474?
The multiple layers of emission appear strangely complex and unexpected given the relatively featureless appearance of the
elliptical galaxy in less deep images.
The cause of the shells is currently unknown, but possibly
tidal tails related to debris left over from absorbing numerous small galaxies in the past billion years.
Alternatively the shells
may be like ripples in a pond,
where the ongoing collision with the spiral galaxy just above
NGC 474
is causing density
waves to ripple through the galactic giant.
Regardless of the actual cause, the
featured image
dramatically highlights the increasing consensus that at least some elliptical
galaxies
have formed in the recent past, and that the outer halos of most
large galaxies are not really smooth
but have complexities induced by frequent
interactions with --
and accretions of --
smaller nearby galaxies.
The halo of our own
Milky Way Galaxy
is
one example of such
unexpected complexity.
NGC 474 spans about 250,000
light years and lies about 100 million light years distant toward the constellation of the Fish
(Pisces).
 APOD: 2018 January 3 - The Helix Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2018 January 3 - The Helix Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
Will our Sun look like this one day?
The Helix Nebula is one of brightest and closest examples of a
planetary nebula, a gas
cloud created at the end of the life of a Sun-like star.
The outer gasses of the star
expelled into space appear from our
vantage point as if we are looking down a helix.
The remnant central stellar core, destined to become a white dwarf star, glows in light so
energetic
it causes the previously expelled gas to fluoresce.
The Helix Nebula, given a technical designation of
NGC 7293,
lies about 700 light-years away towards the
constellation of the Water Bearer (Aquarius)
and spans about 2.5 light-years.
The featured picture was taken with the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) located atop a dormant volcano in Hawaii,
USA.
A close-up of the
inner edge of the Helix Nebula shows complex gas knots of
unknown origin.
 APOD: 2017 December 27 - The Horsehead Nebula
APOD: 2017 December 27 - The Horsehead Nebula
Explanation:
One of the most identifiable nebulae in the sky,
the Horsehead Nebula in Orion, is part of a large, dark,
molecular cloud.
Also known as Barnard 33, the unusual shape was first
discovered on a
photographic plate in the late 1800s.
The red glow originates from
hydrogen
gas predominantly behind the nebula, ionized by the nearby bright star
Sigma Orionis.
The darkness of the
Horsehead is caused mostly by thick
dust,
although the lower part of the
Horsehead's neck casts a shadow to the left.
Streams of gas leaving
the nebula are funneled by a strong
magnetic field.
Bright spots in the
Horsehead Nebula's base are
young stars just in the process of forming.
Light takes about 1,500 years to reach us from the
Horsehead Nebula.
The featured image was taken with the large 3.6-m
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope
in Hawaii,
USA.
 APOD: 2009 August 31 - Open Cluster M25
APOD: 2009 August 31 - Open Cluster M25
Explanation:
Many stars like our Sun were formed in open clusters.
The
above pictured open cluster,
M25,
contains thousands of stars and is about two thousand
light years distant.
The stars in this cluster all formed together about 90 million years ago.
The bright young stars in
M25
appear blue.
Open clusters,
also called galactic clusters, contain fewer and younger stars than
globular clusters.
Also unlike
globular clusters,
open clusters
are generally confined to the
plane of our Galaxy.
M25 is visible with
binoculars towards the
constellation of the Archer
(
Sagittarius).
 APOD: 2009 April 13 - Star Trails over the Canada France Hawaii Telescope
APOD: 2009 April 13 - Star Trails over the Canada France Hawaii Telescope
Explanation:
Just fix your camera to a tripod and you too can make an image of
graceful trails traced by the stars as planet Earth rotates on its axis.
Making a time lapse video like that
shown above may require more effort, though.
Made on 2006 October 13 from
Mauna Kea,
Hawaii,
USA,
this video nicely captured what you might see of the night sky if you could keep your brain from changing your
perceived visual image about every hundredth of a second.
Starting from a dark sky and point-like stars, the video demonstrates how stars appear to move over the night as the
world turns.
Near the center of the developing
bull's-eye
pattern is
Polaris, the North Star.
Visible in the left foreground is the 3.7-meter aperture
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT).
The red glow that illuminated the
CFHT dome near the beginning of the film was created by a car leaving the
volcanic summit.
The Moon rose about half way through the video and created a white glow that gradually illuminated most of the CFHT dome.
The above remarkable time-lapse video was constructed from about 1,000 consecutive frames taken with a digital camera over nearly nine hours.
 APOD: 2008 September 9 - M110: Satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy
APOD: 2008 September 9 - M110: Satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy
Explanation:
Our Milky Way Galaxy is not alone.
It is part of a gathering of about 25 galaxies known as the
Local Group.
Members include the
Great Andromeda Galaxy (M31),
M32,
M33, the
Large Magellanic Cloud, the
Small Magellanic Cloud,
Dwingeloo 1, several small
irregular galaxies,
and many
dwarf elliptical and
dwarf spheroidal galaxies.
Pictured
on the lower right is one of the
dwarf
ellipticals:
NGC 205.
Like
M32,
NGC 205
is a companion to the large M31,
and can sometimes be seen to the south of
M31's center in photographs.
The image shows
NGC 205 to be unusual
for an elliptical galaxy
in that it contains at least two
dust clouds
(at 9 and 2 o'clock - they are visible but hard to spot)
and signs of recent star formation.
This galaxy is sometimes known as M110,
although it was actually not part of
Messier's original
catalog.
 APOD: 2008 May 20 - The Perseus Cluster of Galaxies
APOD: 2008 May 20 - The Perseus Cluster of Galaxies
Explanation:
Here is one of the
largest objects that anyone will ever see on the sky.
Each of these fuzzy blobs is a galaxy, together making up the
Perseus Cluster, one of the closest
clusters
of galaxies.
The cluster is seen through a foreground of faint stars in our own
Milky Way Galaxy.
Near the cluster center, roughly 250 million light-years
away, is the cluster's dominant galaxy NGC 1275,
seen above as the large galaxy on the image left.
A prodigious source of
x-rays and radio emission,
NGC 1275 accretes
matter as gas and galaxies fall into it.
The Perseus Cluster of Galaxies
is part of the Pisces-Perseus supercluster
spanning over 15 degrees and containing over 1,000 galaxies.
At the distance of NGC 1275, this view covers about 7.5 million
light-years.
 APOD: 2008 April 22 - The Fox Fur Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2008 April 22 - The Fox Fur Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
This interstellar beast
is formed of cosmic dust and
gas interacting
with the energetic light and winds from hot young stars.
The shape, visual texture, and color, combine to give the region
the popular name
Fox Fur Nebula.
The characteristic blue glow on the left is dust reflecting light
from the bright star
S Mon,
just beyond the left edge of
the image.
Mottled pink and brown areas
are a combination of the cosmic dust and reddish emission from
ionized hydrogen gas.
S Mon is part of a young
open cluster of stars,
NGC 2264, located
about 2,500
light years away toward the
constellation of
Monoceros,
just north of the Cone Nebula.
 APOD: 2008 April 2- Globular Cluster M55 from CFHT
APOD: 2008 April 2- Globular Cluster M55 from CFHT
Explanation:
The fifty-fifth entry in Charles
Messier's catalog,
M55 is
a large and lovely
globular cluster
of around 100,000 stars.
Only 20,000 light-years away in the constellation
Sagittarius,
M55 appears to earth-bound observers to be nearly 2/3 the size
of the full moon.
Globular star clusters like M55
roam the halo of our Milky Way Galaxy as gravitationally bound populations of stars
known to be much older than stellar groups found in the Galactic disk.
Astronomers who make
detailed studies
of globular cluster stars
can accurately measure the cluster ages and distances.
Their results ultimately constrain the age
of the
Universe (... it must be older than the stars in it!),
and provide a fundamental rung on the
astronomical
distance ladder.
This stunning color image was made with the 3.6 meter
CFHT telescope and
spans about 100 light-years across the globular cluster M55.
 APOD: 2008 January 14 - The Cocoon Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2008 January 14 - The Cocoon Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
What creates the colors of the Cocoon Nebula?
The Cocoon Nebula, cataloged as
IC 5146, is a
strikingly beautiful nebula located about 4,000 light years away toward the constellation of the Swan
(Cygnus).
Inside the
Cocoon Nebula is a newly developing
open cluster
of stars.
Like other
stellar nurseries,
the Cocoon Nebula holds, at the same time, a bright red
emission nebula, blue
reflection nebulas, and dark
absorption nebulas.
Given different mixtures, these three processes create a host of colors in
this image taken recently by the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT) in
Hawaii, USA.
Speculation based on
recent measurements holds
that the massive star towards the left of
the picture opened a hole in an existing
molecular cloud
through which much of the glowing material flows.
The same star, which formed about 100,000 years ago,
now provides the energy source for much of the emitted and
reflected light from this nebula.
 APOD: 2007 November 21 - Expansive Comet Holmes
APOD: 2007 November 21 - Expansive Comet Holmes
Explanation:
The spherical coma of Comet Holmes has swollen
to a diameter of over 1.4 million kilometers, making the
tenuous, dusty cloud even
bigger
than the Sun.
Scattering sunlight, all that dust and gas came from the comet's
remarkably
active nucleus, whose diameter before
the late October
outburst was estimated to be a
mere 3.4 kilometers.
In this sharp image, recorded on November 14 with
the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope,
stars are easily visible right through the outer
coma,
while the
nucleus is buried inside the condensed,
bright region.
The bright region of the coma seems offset from
the center, consistent with the idea that a
large fragment drifted away from the nucleus
and disintegrated, producing the comet's spectacular outburst.
Of course, more
recent
images of Holmes also
show the bright star Mirfak (Alpha Persei) shining through
as the comet sweeps slowly through the constellation
Perseus.
 APOD: 2007 June 11 - The Merope Reflection Nebula
APOD: 2007 June 11 - The Merope Reflection Nebula
Explanation:
Reflection nebulas reflect light from a nearby star.
Many small carbon
grains in the nebula reflect the light.
The blue color typical of reflection nebula is caused by blue light being
more efficiently scattered by the carbon
dust than red light.
The brightness of the nebula is determined by the
size and density of the reflecting grains,
and by the color and brightness of the neighboring star(s).
NGC 1435,
pictured above, surrounds
Merope (23 Tau), one of the brightest stars in the
Pleiades (M45).
The Pleiades nebulosity is caused by a
chance encounter between an
open cluster of stars and a
molecular cloud.
 APOD: 2007 March 14 - Barred Spiral Galaxy M95
APOD: 2007 March 14 - Barred Spiral Galaxy M95
Explanation:
Why do some spiral galaxies have a ring around the center?
First and foremost,
M95 is one of the
closer examples of a big and beautiful barred
spiral galaxy.
Visible in the
above recent image from the
CFHT telescope in
Hawaii,
USA, are sprawling
spiral arms delineate by
open clusters of bright blue stars, lanes of
dark dust, the diffuse glow of billions of faint stars,
and a short bar across the galaxy center.
What intrigues many astronomers, however, is the circumnuclear
ring around the galaxy center visible just outside the
central bar.
Recent images by the
Chandra X-ray Observatory have shown that
X-ray light
surrounding the ring is likely emission from recent
supernovas.
Although the long term stability of the ring remains a
topic of research,
recent observations indicate its present brightness is at least enhanced by
transient bursts of star formation.
M95,
also known as NGC 3351, spans about 50,000
light-years and can be seen with a small telescope toward the constellation of the Lion
(Leo).
 APOD: 2007 January 30 - Thor's Helmet from CFHT
APOD: 2007 January 30 - Thor's Helmet from CFHT
Explanation:
NGC 2359 is a striking emission nebula with an impressive popular name - Thor's
Helmet
Sure, its suggestive winged appearance might lead some to refer
to it as the "duck nebula", but if you were a nebula which name
would you choose?
By any name NGC 2359 is a bubble-like nebula some 30 light-years
across, blown by energetic winds from an extremely
hot star seen near
the center and classified as a Wolf-Rayet star.
Wolf-Rayet stars
are rare massive blue giants which develop
stellar winds
with speeds of millions of kilometers per hour.
Interactions with a nearby large
molecular cloud are thought
to have contributed to this nebula's more complex shape and
curved bow-shock structures.
NGC 2359
is about 15,000 light-years distant toward
the constellation
Canis Major.
 APOD: 2006 July 4 - Elliptical Galaxy Centaurus A from CFHT
APOD: 2006 July 4 - Elliptical Galaxy Centaurus A from CFHT
Explanation:
Why is peculiar galaxy Centaurus A so dusty?
Dramatic dust lanes that run
across the galaxy's center mark
Cen A.
These dust lanes are so thick they almost completely obscure the
galaxy's center in
visible light.
This is particularly unusual as
Cen A's
red stars and round shape are characteristic of a giant
elliptical galaxy,
a galaxy type usually low in dark dust.
Cen A,
also known as NGC 5128, is also unusual compared to an average
elliptical galaxy because it contains a
higher proportion of young blue stars and is a
very strong source of
radio emission.
Evidence indicates that
Cen A is likely the result of the
collision of two
normal galaxies.
During the collision, many
young stars were formed, but
details of the creation of
Cen A's unusual dust belts are still being researched.
Cen A lies only 13 million
light years away, making it the closest
active galaxy.
Cen A,
pictured above, spans 60,000 light years and can be
seen with binoculars toward the constellation of
Centaurus.
 APOD: 2006 February 28 - The Flaming Star Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2006 February 28 - The Flaming Star Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
Rippling dust and gas lanes give the Flaming Star Nebula its name.
The red and purple colors of the nebula are present in
different regions and are created by different processes.
The bright star AE Aurigae,
visible toward the image left, is so hot it is blue,
emitting light so energetic it knocks
electrons away from surrounding gas.
When a proton recaptures an electron,
red light is frequently emitted.
The purple region's color is a mix of this
red light and blue light emitted by AE
Aurigae
but reflected to us by surrounding dust.
The two regions are referred to as
emission nebula and
reflection nebula, respectively.
Pictured above,
the Flaming Star Nebula, officially known as
IC 405, lies about 1500
light years distant, spans about 5 light years,
and is visible with a small telescope toward the constellation of the Charioteer
(Auriga).
 APOD: 2005 December 29 - The Iris Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2005 December 29 - The Iris Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
Like delicate cosmic petals, these clouds of interstellar
dust and gas have blossomed 1,300 light-years away in the fertile
star fields of the constellation Cepheus.
Sometimes called the Iris Nebula and dutifully
cataloged as NGC
7023, this is not the only nebula in the
sky to evoke the imagery of flowers.
Still, this beautiful digital image shows off the Iris Nebula's range of colors and
symmetries in impressive detail.
Within the Iris, dusty nebular material surrounds a massive, hot,
young star in its formative years.
Central filaments of cosmic dust glow with a reddish
photoluminescence
as some dust grains
effectively
convert the star's invisible
ultraviolet
radiation to visible red light.
Yet the dominant color of the nebula is blue,
characteristic
of dust grains reflecting starlight.
Dark, obscuring clouds of dust and
cold molecular gas are also
present and can lead the eye to see other
convoluted and
fantastic shapes.
Infrared observations
indicate that this nebula may contain complex carbon molecules known as
PAHs.
As shown here, the
Iris
Nebula is about 6
light-years across.
 APOD: 2005 November 22 - A Galactic Collision in Cluster Abell 1185
APOD: 2005 November 22 - A Galactic Collision in Cluster Abell 1185
Explanation:
What is a guitar doing in a cluster of galaxies? Colliding.
Clusters of galaxies are sometimes packed so tight that the
galaxies that compose them
collide.
A prominent example occurs on the left of the
above image of the rich
cluster of galaxies Abell 1185.
There at least two galaxies, cataloged as
Arp 105 and dubbed
The Guitar
for their familiar appearance, are pulling each other apart gravitationally.
Most of Abell 1185's hundreds of galaxies are
elliptical galaxies, although
spiral,
lenticular, and
irregular galaxies are all clearly evident.
Many of the spots on the above image are fully galaxies themselves containing
billions of stars, but some spots are foreground stars in our own
Milky Way Galaxy.
Recent observations of
Abell 1185 have found unusual globular clusters of stars that appear to belong
only to the galaxy cluster and not to any individual galaxy.
Abell 1185 spans about one million
light years and lies 400 million light years distant.
 APOD: 2005 July 4 - A Panorama from Mauna Kea
APOD: 2005 July 4 - A Panorama from Mauna Kea
Explanation:
Typically, views from Mauna Kea are up and dark.
That's because the
famous dormant volcano in
Hawaii is arguably
Earth's premier observing platform of the complex
and ever changing night sky.
However, this
daytime view is across and bright.
White snow and white clouds seem to blend together to make an
alien landscape.
Cinder cones from extinct volcanic outbursts dominate the foreground.
Scrolling right will reveal structures visually incongruous even here: an
armada of the
largest
optical telescopes on Earth.
The observatories seen include
Subaru and
Keck.
In the distance on the far left is
Mauna Loa,
Earth's largest volcano.
 APOD: 2005 June 27 - Globular Cluster M22 from CFHT
APOD: 2005 June 27 - Globular Cluster M22 from CFHT
Explanation:
The globular cluster
M22,
pictured above, contains over 100,000 stars.
These stars formed together and are gravitationally bound.
Stars orbit the center
of the cluster, and the cluster orbits the
center of our Galaxy.
So far, about
140 globular clusters are known to exist in a roughly
spherical halo around the
Galactic center.
Globular clusters
do not appear spherically distributed as viewed from the Earth,
and this fact was a key point in the
determination that our Sun
is not at the center of
our Galaxy.
Globular clusters are very old.
There is a straightforward method of
determining their age, and this nearly matches the
13.7 billion-year age of our
entire universe.
 APOD: 2005 May 31 - The Trifid Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2005 May 31 - The Trifid Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
Unspeakable beauty and unimaginable bedlam can be found
together in the
Trifid Nebula.
Also known as M20,
this photogenic nebula is visible
with good binoculars towards the constellation of Sagittarius.
The energetic processes of
star formation create not only the colors but the
chaos.
The red-glowing gas
results from high-energy starlight striking interstellar
hydrogen gas.
The dark dust
filaments that lace
M20 were created in the atmospheres of cool
giant stars and in the debris from
supernovae explosions.
Which bright young stars light up the blue
reflection nebula is still
being investigated.
The light from
M20 we see today left perhaps 3000 years ago,
although the exact distance remains unknown.
Light takes about 50 years to cross
M20.
 APOD: 2005 May 9 - Stars, Dust and Nebula in NGC 6559
APOD: 2005 May 9 - Stars, Dust and Nebula in NGC 6559
Explanation:
When stars form, pandemonium reigns.
A textbook
case is the star forming region
NGC 6559.
Visible above are red glowing
emission nebulas of
hydrogen, blue
reflection nebulas of
dust, dark
absorption nebulas of dust, and the stars that formed from them.
The first massive stars formed from the dense gas will emit
energetic light and
winds
that erode, fragment, and
sculpt their birthplace.
And then they
explode.
The resulting morass
can be as beautiful as it is complex.
After tens of millions of years, the dust boils away,
the gas gets swept away, and all that is left is a naked
open cluster of stars.
 APOD: 2005 February 13 - In the Center of the Virgo Cluster
APOD: 2005 February 13 - In the Center of the Virgo Cluster
Explanation:
The Virgo Cluster of Galaxies
is the closest cluster of galaxies to our
Milky Way Galaxy.
The Virgo Cluster is so close that it spans more than 5 degrees on the sky - about 10 times the angle made by a
full Moon.
It contains over 100
galaxies of many types - including
spiral,
elliptical, and
irregular galaxies.
The Virgo Cluster is so massive that it is noticeably
pulling our Galaxy toward it.
The cluster contains not only galaxies filled with stars but also
gas so hot it glows in
X-rays.
Motions of galaxies in and around clusters
indicate that they contain more
dark matter than any visible matter we can see.
Pictured above, the center of the
Virgo cluster
might appear to some as a human face, and includes bright
Messier galaxies
M86 at the top,
M84 on the far right,
NGC 4388 at the bottom, and
NGC 4387 in the middle.
 APOD: 2004 December 8 - In the Center of the Heart Nebula
APOD: 2004 December 8 - In the Center of the Heart Nebula
Explanation:
What powers the Heart Nebula?
The large emission nebula dubbed
IC 1805 looks, in whole, like a
human heart.
The nebula glows brightly in red light
emitted by its most prominent element:
hydrogen.
The red glow and the larger shape are all created by a
small group of stars near the nebula's center.
A close up spanning about 30 light years contains many of these stars is
shown above in a recent image taken by the
Canada France Hawaii Telescope.
This open cluster of stars
contains a few bright stars nearly 50 times the mass of our Sun,
many dim stars only a fraction of the mass of our Sun, and an
absent microquasar
that was expelled millions of years ago.
The Heart Nebula is located about 7,500
light years away toward the
constellation of
Cassiopeia.
 APOD: 2004 October 4 - NGC 6823: Cloud Sculpting Star Cluster
APOD: 2004 October 4 - NGC 6823: Cloud Sculpting Star Cluster
Explanation:
Star cluster NGC 6823 is ready for its close-up.
The center of the open cluster,
visible on the upper right,
formed only about two million years ago and is
dominated in brightness by a host of
bright young blue stars.
Outer parts of the cluster,
visible above in the image center
as the stars and pillars of
emission nebula
NGC 6820, contain even younger stars.
The huge pillars of gas and
dust likely get their elongated shape by
erosion from hot radiation emitted from the
brightest cluster stars.
Striking dark globules
of gas and dust are also visible across the bottom of this image by the
25 year old
Canada France Hawaii Telescope.
Open star cluster
NGC 6823 spans
about 50 light years and lies about 6000
light years away toward the
constellation of Vulpecula (The Fox).
 APOD: 2004 August 16 - Close Up of the Lagoon Nebula
APOD: 2004 August 16 - Close Up of the Lagoon Nebula
Explanation:
Stars are battling gas and dust in the Lagoon Nebula
but the photographers are winning.
Also known as M8,
this photogenic nebula is visible
even without binoculars towards the constellation of Sagittarius.
The energetic processes of
star formation create not
only the colors but the
chaos.
The
red-glowing gas
results from high-energy starlight striking interstellar
hydrogen gas.
The dark
dust
filaments that lace
M8 were created in
the atmospheres of cool
giant stars and in the
debris from
supernovae explosions.
This spectacular portion of the
Lagoon Nebula taken by the
CFHT was created from light emitted by hydrogen (shown in red) and light emitted by
oxygen
(shown in green).
The light from
M8 we see today left about 5000 years ago.
Light takes about 50 years to cross this section of
M8.
 APOD: 2004 June 16 - Elliptical Galaxy M87
APOD: 2004 June 16 - Elliptical Galaxy M87
Explanation:
Elliptical galaxy
M87 is a type of
galaxy that looks much different than our own
Milky Way Galaxy.
Even for an
elliptical galaxy,
though, M87 is peculiar.
M87 is much bigger than an average galaxy, appears near the
center of a whole
cluster of galaxies known as the
Virgo Cluster,
and shows an unusually high number of globular clusters.
These globular clusters
are visible as faint spots surrounding the bright center of
M87.
In general,
elliptical galaxies contain similar numbers of stars as
spiral galaxies, but are ellipsoidal in shape (spirals are mostly flat), have no spiral structure, and little
gas and
dust.
The
above image of M87 was taken recently by the
Canada-France-Hawaii
Telescope
on top of the dormant volcano
Mauna Kea in
Hawaii,
USA.
 APOD: 2004 April 7 - Unusual Spiral Galaxy M66
APOD: 2004 April 7 - Unusual Spiral Galaxy M66
Explanation:
Why isn't spiral galaxy
M66 symmetric?
Usually
density waves of gas, dust, and newly formed stars circle a
spiral galaxy's
center and create a
nearly symmetric galaxy.
The differences between
M66's
spiral arms and the apparent displacement of its
nucleus are all likely caused by the
tidal gravitational pull of nearby galaxy neighbor
M65.
Spiral galaxy M66,
pictured above, spans about 100,000
light years, lies about 35 million light years distant, and is the largest galaxy in a
group including
M65 and
NGC 3628 known as the
Leo Triplet.
Like many spiral galaxies, the long and intricate
dust lanes of
M66 are seen intertwined with the
bright stars and
nebulas
that light up the spiral arms.
 APOD: 2004 March 15 - The Orion Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2004 March 15 - The Orion Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
Few astronomical sights excite the imagination like the
nearby stellar nursery known as the
Orion Nebula.
The Nebula's glowing gas surrounds hot young stars at
the edge of an immense interstellar
molecular cloud only 1500 light-years away.
The Great Nebula in Orion can be
found with the unaided eye just below and to the left of the
easily identifiable
belt of three stars in the popular constellation Orion.
The above image from the
3.6-meter Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope atop a
dormant volcano in Hawaii brings out
Orion's detail in spectacular fashion.
Buried in the complex nebulosity are the bright stars of the
Trapezium in
Orion's heart, the sweeping lanes of
dark dust that cross the center,
the pervasive red glowing hydrogen gas,
and the
blue tinted dust
that reflects the light of newborn stars.
The whole Orion Nebula cloud complex, which includes the
Horsehead Nebula,
will slowly disperse over the next 100,000 years.
 APOD: 2004 January 28 - The Crab Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2004 January 28 - The Crab Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
This is the mess that is left when a star explodes.
The Crab Nebula, the result of a
supernova seen in
1054 AD,
is filled with mysterious filaments.
The filaments are not only
tremendously complex, but appear to have
less mass than expelled
in the original supernova and a
higher speed than expected
from a free explosion.
The above image, taken by the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (CFHT),
is in three colors chosen for scientific interest.
The Crab Nebula spans about 10 light-years.
In the nebula's very center lies a
pulsar: a
neutron star as massive as the
Sun
but with only the size of a
small town.
The Crab Pulsar
rotates about 30 times each second.
 APOD: 2003 December 15 - Open Star Clusters M35 and NGC 2158
APOD: 2003 December 15 - Open Star Clusters M35 and NGC 2158
Explanation:
Open clusters of stars can be near or far, young or old,
and diffuse or compact.
Open clusters
may contain from 100 to 10,000 stars, all of which formed at
nearly the same time.
Bright blue stars frequently
distinguish younger open clusters.
M35,
pictured above on the upper left, is relatively nearby at 2800 light years distant, relatively young at 150 million years old,
and relatively diffuse, with about 2500 stars spread out over a
volume 30 light years across.
An older and more compact open cluster,
NGC 2158, is
visible above on the lower right.
NGC 2158 is four times more distant that
M35, over 10 times older, and much more compact as it contains many
more stars in roughly the same volume of space.
NGC 2158's bright blue stars have
self-destructed,
leaving cluster light to be dominated by
older and yellower stars.
Both clusters are visible toward the constellation of Gemini -- M35 with binoculars and NGC 2158 with a small telescope.
 APOD: 2003 October 19 - An Unusual Globule in IC 1396
APOD: 2003 October 19 - An Unusual Globule in IC 1396
Explanation:
Is there a monster in IC 1396?
Known to some as the
Elephant's Trunk Nebula, parts of gas and
dust clouds of this
star formation region
may appear to take on foreboding forms, some
nearly human.
The only real
monster here, however, is a
bright young star too far from Earth to hurt us.
Energetic light from this star is eating away the dust of the dark
cometary globule near the top of the
above image.
Jets and
winds of particles
emitted from this star are also pushing away ambient gas and
dust.
Nearly 3,000 light-years distant, the relatively faint
IC 1396 complex covers a much larger region on the
sky than shown here, with an apparent width of more than 10
full moons.
 APOD: 2003 October 7 - The Colorful Horsehead Nebula
APOD: 2003 October 7 - The Colorful Horsehead Nebula
Explanation:
While drifting through the cosmos, a magnificent interstellar
dust cloud became sculpted by stellar winds and radiation to
assume a recognizable shape.
Fittingly named the Horsehead Nebula, it is embedded in the vast and complex
Orion Nebula.
The dark
molecular cloud, roughly 1,500 light years distant, is cataloged as
Barnard 33
and is visible only because its obscuring dust is
silhouetted against the bright
emission nebula IC 434.
The bright blue
reflection nebula
NGC 2023 is visible on the lower left.
The prominent horse head
portion of the nebula is really just part of a
larger cloud of
dust which can be seen extending
toward the bottom of the picture.
A potentially rewarding but difficult object to view with a
small telescope, this gorgeous
representative-color image was taken by the large 3.6-m
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope
in Hawaii,
USA.
 APOD: 2003 September 3 - Galactic Supernova Remnant IC 443
APOD: 2003 September 3 - Galactic Supernova Remnant IC 443
Explanation:
About 8000 years ago, a star in
our Galaxy exploded.
Ancient humans might have noticed the
supernova as a temporary star, but
modern humans can see the expanding shell of gas even today.
Pictured above, part of the shell of
IC 443 is seen to be composed of
complex filaments,
some of which are impacting an existing
molecular cloud.
Here emission from
shock-excited
molecular
hydrogen is allowing astronomers to study how fast moving
supernova gas affects star formation in the cloud.
Additionally, astronomers theorize that the
impact accelerates some particles to velocities near the speed of light.
Supernova remnant
IC 443 is also known to shine brightly also in
infrared and
X-ray light.
 APOD: 2003 August 4 - In the Center of the Virgo Cluster
APOD: 2003 August 4 - In the Center of the Virgo Cluster
Explanation:
The Virgo Cluster of Galaxies
is the closest cluster of galaxies to our
Milky Way Galaxy.
The Virgo Cluster is so close that it spans more than 5
degrees on the sky - about 10 times the angle made by a
full Moon.
It contains over 100
galaxies of many types - including
spiral,
elliptical, and
irregular galaxies.
The Virgo Cluster is so massive that it is noticeably
pulling our Galaxy toward it.
The cluster contains not only galaxies filled with stars but also
gas so hot it glows in
X-rays.
Motions of galaxies in and around clusters
indicate that they contain more
dark matter than any visible matter we can see.
Pictured above, the center of the
Virgo cluster
might appear to some as a human face, and includes bright
Messier galaxies
M86 at the top,
M84 on the far right,
NGC 4388 at the bottom, and
NGC 4387 in the middle.
 APOD: 2003 May 25 - Spiral Galaxy NGC 253 Almost Sideways
APOD: 2003 May 25 - Spiral Galaxy NGC 253 Almost Sideways
Explanation:
NGC 253 is a normal
spiral galaxy seen here almost sideways.
It is the largest member of the
Sculptor Group of Galaxies, the nearest
group to our own
Local Group of Galaxies.
NGC 253,
pictured above, appears visually as one of the brightest
spirals on the sky,
and is easily visible in
southern hemisphere
with a good pair of binoculars.
The type Sc galaxy is about 10 million light years distant.
NGC 253 is considered a
starburst galaxy because of high star formation rates
and dense dust
clouds in its nucleus.
The energetic nuclear region is seen to glow in
X-ray and
gamma-ray light.
 APOD: 2003 April 7 - NGC 281: Cluster, Clouds, and Globules
APOD: 2003 April 7 - NGC 281: Cluster, Clouds, and Globules
Explanation:
NGC 281 is a busy workshop of star formation.
Prominent features include a small
open cluster of stars,
a diffuse red-glowing
emission nebula, large lanes of obscuring
gas and
dust, and dense knots
of dust and gas in which stars may still be forming.
The open cluster
of stars IC 1590 visible around the center
has formed only in the last few million years.
The brightest member of this cluster is actually a
multiple-star system
shining light that helps ionize the nebula's gas,
causing the red glow visible throughout.
The lanes of dust
visible below the center are likely homes
of future star formation.
Particularly striking in the
above photograph are the dark
Bok globules
visible against the bright nebula.
Stars are surely forming there right now.
The entire
NGC 281 system lies about 10 thousand light years distant.
 APOD: 2003 March 10 - M101: The Pinwheel Galaxy
APOD: 2003 March 10 - M101: The Pinwheel Galaxy
Explanation:
Why do many galaxies appear as
spirals?
A striking example is M101,
shown above, whose relatively close distance of about 22 million light years allow it to be studied in some detail.
Recent evidence indicates that a
close gravitational interaction with a neighboring galaxy created
waves of high mass and condensed gas which
continue to orbit the galaxy center.
These waves compress existing gas and cause star formation.
One result is that
M101, also called the
Pinwheel Galaxy, has several extremely
bright star-forming regions
(called HII regions) spread across its spiral arms.
M101 is so large that its
immense gravity distorts smaller nearby galaxies.
 APOD: 2003 February 13 - The Eagle Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2003 February 13 - The Eagle Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
Bright blue stars are still forming in the
dark pillars of the
Eagle Nebula.
Made famous by a
picture from the
Hubble Space Telescope in 1995, the
Eagle Nebula shows the dramatic process of star formation.
To the upper right of the nebula in the
above picture lies the heart of the
open cluster M16.
The bright blue stars of
M16 have been continually forming over the past 5 million years,
most recently in the famous central
gas and
dust pillars known as
elephant trunks.
Light takes about 7000 years to reach us from
M16, which spans about 20
light years and
can be seen
with binoculars toward the constellation of
Serpens.
 APOD: 2003 January 22 - M11: The Wild Duck Cluster
APOD: 2003 January 22 - M11: The Wild Duck Cluster
Explanation:
Many
stars like our
Sun were formed in
open clusters.
The above pictured open cluster,
M11, contains thousands of stars and is just over
five thousand
light years distant.
The stars in this cluster all formed
together about 250 million years ago.
The bright young stars in
M11 appear blue.
Open clusters, also
called galactic clusters, contain fewer and younger stars than
globular clusters.
Also unlike
globular clusters,
open clusters are generally confined to the plane of
our Galaxy.
M11 is visible with binoculars towards the constellation of Scutum.
 APOD: 2002 December 10 - M17: Omega Nebula Star Factory
APOD: 2002 December 10 - M17: Omega Nebula Star Factory
Explanation:
In the depths of the
dark clouds of
dust and
molecular gas known as
M17,
stars continue to form.
The similarity to the
Greek letter capital Omega gives the
molecular cloud its popular name, but the nebula is
also known as the Swan Nebula, the Horseshoe Nebula, and M17.
The darkness of these
molecular clouds results from background starlight
being absorbed by thick carbon-based smoke-sized
dust.
As bright
massive stars form,
they produce intense and
energetic light that
slowly boils away the dark shroud.
M17, pictured above,
is visible with binoculars towards the
constellation of Sagittarius, lies 5000
light-years away, and spans 20 light-years across.
 APOD: 2002 October 14 - IC 5146: The Cocoon Nebula
APOD: 2002 October 14 - IC 5146: The Cocoon Nebula
Explanation:
How did this nebula get created?
The Cocoon Nebula, cataloged as
IC 5146, is a
strikingly beautiful nebula located about 4,000 light years away toward the constellation of
Cygnus.
Inside the Cocoon is a newly developing
open cluster
of stars.
Like other
stellar nurseries,
the Cocoon Nebula is, at the same time, an
emission nebula, a
reflection nebula, and an
absorption nebula.
Speculation based on recent measurements holds
that the massive star in the center of the
above image opened a hole in an existing
molecular cloud
through which much of the glowing material flows.
The same star, which formed about 100,000 years ago,
now provides the energy source for much of the emitted
and reflected light from this nebula.
 APOD: 2002 July 22 - Open Cluster NGC 6520 from CFHT
APOD: 2002 July 22 - Open Cluster NGC 6520 from CFHT
Explanation:
Did you ever have a day when it felt like
a dark cloud
was following you around?
For the open cluster of stars NGC 6520,
every day is like this.
On the left of the
above picture are many of
NGC 6520's bright blue stars.
They formed only millions of years ago - much more
recently than our ancient Sun which formed billions of years ago.
On the right is an
absorption nebula,
molecular cloud
Barnard 86, from which the stars
of NGC 6520 surely formed.
This nebula contains much opaque
dust that blocks
light from the many stars that
would have been visible in the background.
Surrounding
NGC 6520 is part of the tremendously dense starscape in the
bulge of our Milky Way Galaxy,
the extended halo of stars that surrounds the
center of our Galaxy.
NGC 6520 spans about 10
light years and lies about
5500 light years away toward the direction of
Sagittarius.
 APOD: 2002 July 3 - Interstellar Dust Bunnies of NGC 891
APOD: 2002 July 3 - Interstellar Dust Bunnies of NGC 891
Explanation:
What is going on in NGC 891?
This galaxy appeared previously to be very similar to our own
Milky Way Galaxy: a spiral galaxy
seen nearly edge-on.
However, recent high-resolution
images of
NGC 891's dust show unusual filamentary patterns
extending well away from its Galactic disk.
This interstellar dust
was probably thrown out of the galactic disk toward the halo by
stellar supernovae explosions.
Because dust is so fragile, its appearance after
surviving disk expulsion can be very telling. Newly discovered phenomena, however, sometimes
appear so complex that more
questions are raised than are answered.
 APOD: 2002 May 20 - East of the Lagoon Nebula
APOD: 2002 May 20 - East of the Lagoon Nebula
Explanation:
To the
east of the Lagoon Nebula is a star field rich in diversity.
On the lower left are clouds rich in
dark dust that
hide background stars and
young star systems still forming.
Dark clouds include
LDN 227 on the left and IC 1275 on the right,
with a bright star near its tip.
On the upper right are
clouds rich in hot glowing gas,
including part of the
emission nebula
NGC 6559.
On the right, between the two regions, is a
nebula reflecting light from a
group of massive blue stars.
The NGC 6559 complex pictured above spans about 3
light years and likely has a common history with the
Lagoon Nebula.
The complex
lies about 5000 light-years away toward the constellation of
Sagittarius.
 APOD: 2002 April 9 - The Snake Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2002 April 9 - The Snake Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
What slithers overhead? The dark winding lanes visible in part of the
constellation of
Ophiuchus belong to the
Snake Nebula.
Also known as
Barnard 72, the
Snake Nebula is a series of
dark absorption clouds made up of
molecular gas and interstellar dust.
Interstellar dust grains -
composed predominantly of
carbon - absorb visible starlight and reradiate much of it in the
infrared.
This absorption causes stars behind the
clouds to be obscured from view, hence the appearance of
starless voids on the sky.
Molecular clouds like the
Snake Nebula are places where
new stars are likely to form.
The Snake Nebula,
pictured above, lies about 650 light-years away and spans the angular width of a
full moon.
 APOD: 2002 March 25 - An Unusual Globule in IC 1396
APOD: 2002 March 25 - An Unusual Globule in IC 1396
Explanation:
Is there a monster in IC 1396?
Known to some as the
Elephant's Trunk Nebula, parts of gas and
dust clouds of this
star formation region
may appear to take on foreboding forms, some
nearly human.
The only real
monster here, however, is a
bright young star too far from Earth to hurt us.
Energetic light from this star is eating away the dust of the dark
cometary globule near the top of the
above image.
Jets and
winds of particles emitted
from this star are also pushing away ambient gas and dust.
Nearly 3,000 light-years distant, the relatively faint
IC 1396 complex covers a much larger region on the
sky than shown here, with an apparent width of more than 10
full moons.
 APOD: 2002 March 17 - NGC 2244: A Star Cluster in the Rosette Nebula
APOD: 2002 March 17 - NGC 2244: A Star Cluster in the Rosette Nebula
Explanation:
In the heart of the
Rosette Nebula
lies a bright
open cluster
of stars that lights up the nebula.
The stars of
NGC 2244 formed from the surrounding gas only
four million years ago and emit light and
wind that define the nebula's appearance today.
High energy light from the
bright young stars of
NGC 2244 ionizes the surrounding
hydrogen gas clouds to create the red
emission nebula appearance.
The hot
wind of particles that streams away from the
cluster stars contributes to an already complex
menagerie of gas and
dust filaments while slowly
evacuating the cluster center.
NGC 2244
measures about 50
light-years across, lies about
4500 light-years away, and is visible with
binoculars towards the
constellation of Monoceros.
 APOD: 2000 October 23 - Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy NGC 205 in the Local Group
APOD: 2000 October 23 - Dwarf Elliptical Galaxy NGC 205 in the Local Group
Explanation:
Our Milky Way Galaxy is not alone.
It is part of a gathering of about 25 galaxies known as the
Local Group.
Members include the
Great Andromeda Galaxy (M31),
M32,
M33, the
Large Magellanic Cloud, the
Small Magellanic Cloud,
Dwingeloo 1, several small
irregular galaxies,
and many
dwarf elliptical and
dwarf spheroidal galaxies.
Pictured on the lower left is one of the many
dwarf ellipticals:
NGC 205.
Like
M32,
NGC 205 is a companion to the large M31,
and can sometimes be seen to the south of
M31's center in photographs.
The above image shows
NGC 205 to be unusual for an
elliptical galaxy
in that it contains at least two
dust clouds
(at 1 and 4 o'clock - they are visible but hard to spot)
and signs of recent star formation.
This galaxy is sometimes known as M110,
although it was actually not part of
Messier's original
catalog.
 APOD: 2000 September 5 - CFHT Star Trails
APOD: 2000 September 5 - CFHT Star Trails
Explanation:
High atop a dormant
volcano in Hawaii, an eye 3.6-meters wide stares at a
faint light on the night sky.
Unlike a human eye, which
collects light for only a fraction of a second at a time, a telescope such as the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope
(CFHT) can collect light for hours.
Faint sources become visible that were previously
beyond human imagination.
These meticulous observations usually take so long, though, that the
Earth's spin causes the telescope to move under the sky.
This spin is visible in the above photograph as
star trails in the background.
The CFHT itself must counter-spin to keep on target.
The enormous size of the
CFHT dome can be gauged by the car in the foreground.
The CFHT is one of the smaller telescopes atop
Mauna Kea.
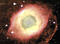 APOD: 2000 August 28 - The Helix Nebula from CFHT
APOD: 2000 August 28 - The Helix Nebula from CFHT
Explanation:
One day our Sun may look like this.
The
Helix Nebula is the
closest example of a
planetary nebula
created at the end of the life of a Sun-like star.
The outer gasses of the star
expelled into space
appear from our vantage point as if we are looking down a
helix.
The remnant central stellar core, destined to become a
white dwarf star, glows in light so
energetic it
causes the previously expelled gas to
fluoresce.
The
Helix Nebula, given a technical designation of
NGC 7293, lies 450
light-years away towards the
constellation of
Aquarius and spans 1.5 light-years.
The
above image was taken with the
Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope
(CFHT) located atop a dormant volcano in
Hawaii, USA.
A close-up of the inner edge
of the
Helix Nebula shows unusual gas knots of
unknown origin.
 APOD: 2000 August 22 - NGC 2244: A Star Cluster in the Rosette Nebula
APOD: 2000 August 22 - NGC 2244: A Star Cluster in the Rosette Nebula
Explanation:
In the heart of the
Rosette Nebula
lies a bright
open cluster
of stars that lights up the nebula.
The stars of
NGC 2244 formed from the surrounding gas only
four million years ago and emit light and
wind that define the nebula's appearance today.
High energy light from the
bright young stars of
NGC 2244 ionizes the surrounding
hydrogen gas clouds to create the red
emission nebula appearance.
The hot
wind of particles that streams away from the
cluster stars contributes to an already complex
menagerie of gas and dust filaments while slowly
evacuating the cluster center.
NGC 2244
measures about 50
light-years across, lies about
4500 light-years away, and is visible with
binoculars towards the
constellation of Monoceros.